Embark on an exciting journey through our solar system’s planets! Discover the secrets of Mercury, Venus, Mars, and more. Dive into the wonders of gas giants like Jupiter and Saturn, and the mysteries of icy planets like Uranus and Neptune. Learn about each planet’s cool features and how they’re different – from scorching hot surfaces to freezing atmospheres. | solar system planets
Solar System Facts | what is solar system | picture of solar system
We’ll also talk about the good stuff, like stunning landscapes and potential for life, as well as the challenges, such as harsh conditions. So if you’re student and curious about space, this guide is for you. Join us in exploring the cosmos and uncovering the incredible stories of these celestial neighbors. Let’s make our journey among the stars together! | planets in solar system
The Luminous Sun: Our Cosmic Hearth

At the center of the solar system reigns the Sun, a dazzling ball of searing-hot gases, primarily hydrogen and helium. With a diameter of about 1.4 million kilometers, the Sun’s immense gravitational pull holds the entire solar system in its thrall. Emitting light, heat, and energy through nuclear fusion, the Sun sustains life on Earth and drives the intricate dance of planets around it.
Mercury: The Swiftest Planet | smallest planet in solar system | closest planet to the Sun
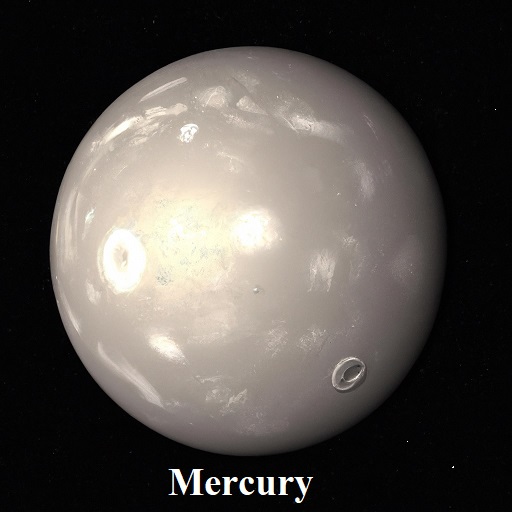

Mercury is the smallest planet in our solar system. It has a diameter of about 4,880 kilometers (3,032 miles), making it just a bit larger than Earth’s Moon. Despite its small size, Mercury is a dense planet with a relatively large iron core, accounting for about 70% of its total mass. It is also the closest planet to the Sun and has a surface that is heavily cratered due to impacts from asteroids and comets.
The closest planet to the Sun, Mercury, boasts the shortest orbit, completing a revolution in just about 88 Earth days. Its proximity to the Sun means that temperatures on Mercury’s surface can soar to scorching highs of around 800 degrees Fahrenheit (427 degrees Celsius) during its day, while plummeting to frigid lows of -290 degrees Fahrenheit (-179 degrees Celsius) at night. Its barren, rocky terrain is pocked with craters, remnants of ancient cosmic collisions.
Venus: The Fiery Planet | hottest planet in solar system
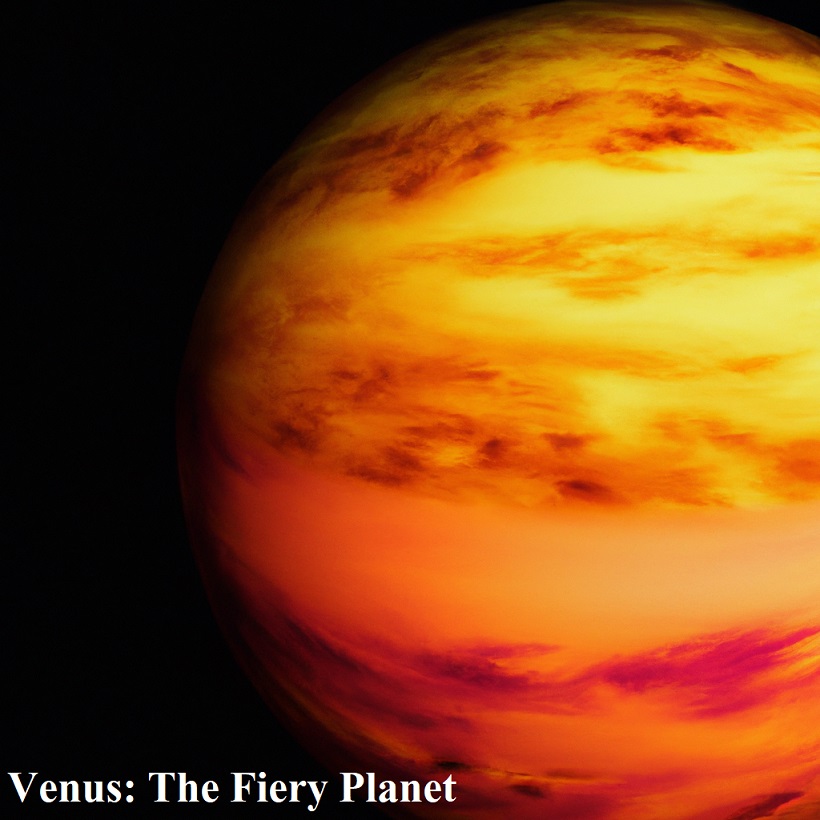

Venus, often referred to as Earth’s “sister planet” due to their similar size, is, in fact, quite inhospitable. Its thick atmosphere traps heat in a runaway greenhouse effect, making it the hottest planet in our solar system. Daytime temperatures can reach up to a blistering 900 degrees Fahrenheit (475 degrees Celsius), hotter than the surface of Mercury, despite being farther from the Sun. Venus’ surface is shrouded in thick clouds of sulfuric acid, obscuring its rugged volcanic landscapes.
Mars: The Red Planet
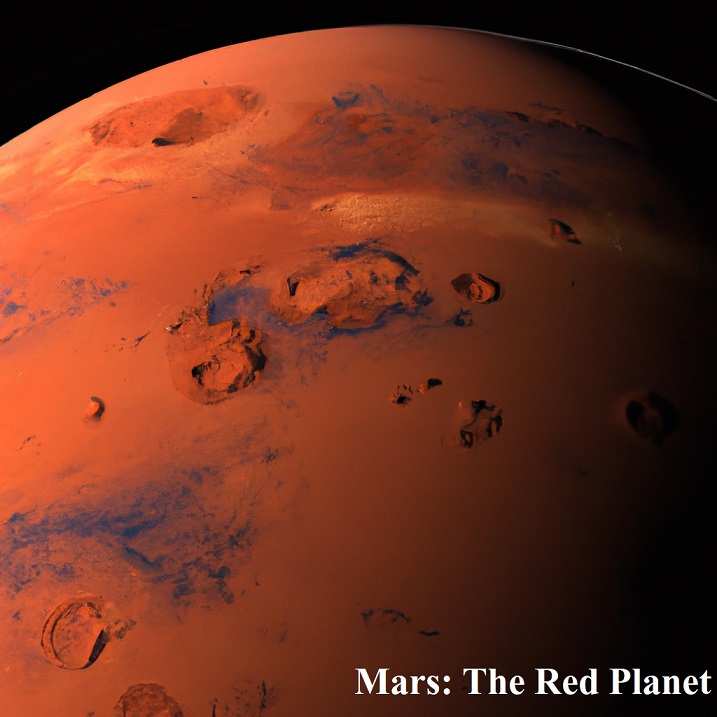

Mars, with its rusty hue, has long captured human imagination. Its days are only slightly longer than Earth’s, lasting about 24.6 hours.
Mars’ temperatures can vary dramatically, with daytime highs around 70 degrees Fahrenheit (20 degrees Celsius) near the equator, but plummeting to a bone-chilling -195 degrees Fahrenheit (-125 degrees Celsius) during the night.
The planet’s thin atmosphere cannot retain heat effectively, contributing to these extreme temperature fluctuations. Mars is known for its diverse landscapes, including expansive deserts, towering volcanoes, and the massive canyon Valles Marineris.
Jupiter: The King of Gas Giants | largest planet in solar system

Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system. It has a diameter of about 139,822 kilometers (86,881 miles), making it more than 11 times wider than Earth. | biggest planet in solar system
Jupiter is a gas giant, primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, and it doesn’t have a solid surface like terrestrial planets.
Its immense size and strong gravitational pull have led to the formation of numerous moons and a complex system of rings. Jupiter’s Great Red Spot, a massive storm, is a well-known feature on its surface.
Jupiter, the largest planet in the solar system, is a gas giant that dwarfs all other planets. Its immense size allows for a day that lasts around 9.9 Earth hours. However, Jupiter’s lack of a solid surface and rapid rotation contribute to its oblate shape.
Despite being far from the Sun, Jupiter’s core generates significant heat, causing the planet to radiate more energy than it receives from the Sun.
Its vibrant bands of clouds, the Great Red Spot, and its many moons, including the four largest known as the Galilean moons, make Jupiter a captivating object of study.
Saturn: The Ringed Wonder

Saturn’s iconic rings, composed of countless particles of ice and rock, make it a standout in the solar system. With a day lasting about 10.7 Earth hours, Saturn rotates on its axis rapidly.
While its stunning rings are a prominent feature, Saturn’s surface is largely composed of gas, and its core is thought to be a mixture of ice, rock, and metal.
The planet’s temperatures are chilly, dropping to around -288 degrees Fahrenheit (-178 degrees Celsius). Saturn’s intricate ring system, made up of numerous distinct rings, continues to intrigue astronomers and scientists.
Uranus: The Sideways Planet
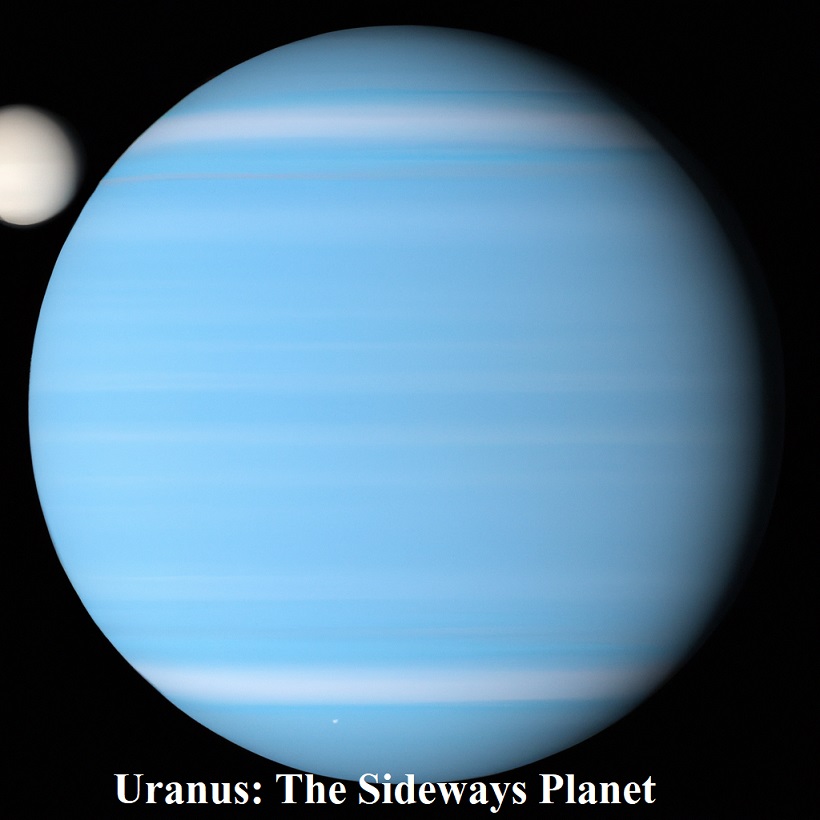

Uranus presents a unique sight with its tilted axis of rotation, causing it to appear to roll on its side as it orbits the Sun. This planet’s day lasts about 17.2 Earth hours.
Uranus is an ice giant, primarily composed of water, methane, and ammonia ices surrounding a rocky core. Its deep blue color is due to the presence of methane in its upper atmosphere.
Uranus experiences extreme seasons due to its axial tilt, resulting in long periods of daylight and darkness. Its temperatures can plunge to as low as -371 degrees Fahrenheit (-224 degrees Celsius).
Neptune: The Mystic Blue Giant | Coldest planet in solar system | Solar System Facts

Neptune, the farthest planet from the Sun, is another ice giant, resembling Uranus in many ways. With a day lasting about 16.1 Earth hours, Neptune’s bluish hue comes from the presence of methane in its atmosphere.
Its temperatures can drop to an astonishingly cold -353 degrees Fahrenheit (-214 degrees Celsius).
Neptune’s dynamic atmosphere features dark spots and storm systems, including the famous Great Dark Spot, reminiscent of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot.
Pluto: The Dwarf Planet | Solar System Facts
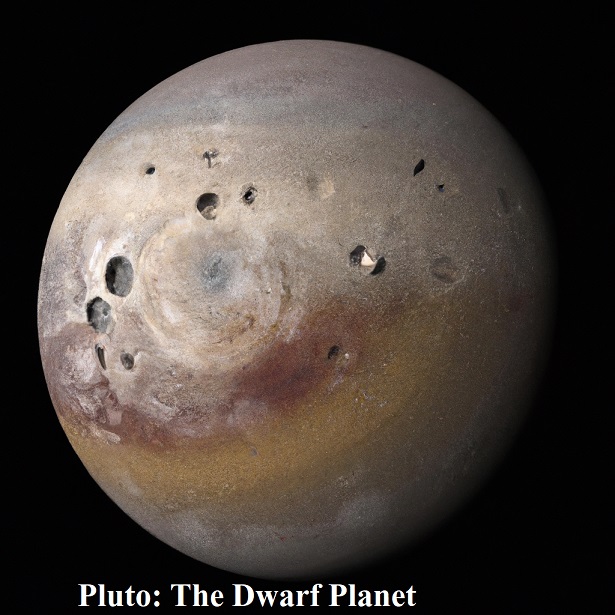

Pluto, once considered the ninth planet, has since been reclassified as a dwarf planet. It orbits the Sun in a highly elliptical orbit and has a day length of about 153.3 Earth hours.
Due to its distant and eccentric orbit, Pluto experiences extreme temperature variations. During its closest approach to the Sun, temperatures can rise to around -375 degrees Fahrenheit (-225 degrees Celsius), while during its farthest point, temperatures can plummet to an even colder -400 degrees Fahrenheit (-240 degrees Celsius).
Pluto’s status as a dwarf planet has spurred debates and discussions about the classification of celestial bodies in the outer solar system.
Solar System Oddities: Moons and Beyond | Solar System Facts | Solar System Facts
Beyond the eight recognized planets, our solar system boasts a myriad of moons, asteroids, comets, and other celestial bodies.
The largest moon in the solar system is Ganymede, a moon of Jupiter, while the dwarf planet Ceres resides in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
Comets like Halley’s Comet and asteroid groups like the Trojans further enrich the diversity of the solar system.
In conclusion, the solar system is a captivating ensemble of celestial objects that revolve around the Sun, each with its unique characteristics and mysteries waiting to be uncovered.
As our understanding of the universe continues to deepen, the exploration of the solar system remains a constant source of fascination and discovery, inviting us to delve further into the secrets of the cosmos. | Solar System Facts
Exploring the Sun: The Heart of the Solar System
The Sun, a colossal sphere of seething gases, holds the solar system in its gravitational embrace. Its core is a crucible of nuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium, releasing an immense amount of energy in the process.
This energy radiates into space in the form of light and heat, sustaining life on Earth and shaping the dynamics of the entire solar system.
The Sun’s surface, known as the photosphere, has a temperature of around 5,500 degrees Celsius (9,932 degrees Fahrenheit).
This layer emits the visible light that reaches our eyes. Above the photosphere lies the chromosphere, a region of gas that appears red during solar eclipses.
Extending even farther is the corona, a faint outer atmosphere that becomes visible during total solar eclipses as a glowing halo around the darkened Sun.
The Sun’s activity is marked by a solar cycle, which lasts about 11 years. During this cycle, the Sun goes through periods of increased and decreased solar activity, leading to changes in the number of sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections.
These events can impact Earth’s space environment and contribute to phenomena like the Northern and Southern Lights.
Day-Night Cycles, Temperatures, and More
Solar System Facts
Understanding the day-night cycles, temperatures, and other aspects of each planet in the solar system provides insights into their unique characteristics and environments.
Mercury
Mercury’s slow rotation on its axis results in an extreme day-night temperature difference. During its scorching daytime, temperatures can reach up to 800 degrees Fahrenheit (427 degrees Celsius). As night falls, temperatures plummet to -290 degrees Fahrenheit (-179 degrees Celsius).
Venus
Venus’ thick atmosphere traps heat, causing it to have a consistent temperature of around 900 degrees Fahrenheit (475 degrees Celsius) day and night due to the greenhouse effect.
Mars
Mars’ relatively similar day length to Earth results in less extreme temperature variations compared to its neighbors. Daytime highs can reach 70 degrees Fahrenheit (20 degrees Celsius) near the equator, but nights can be bone-chilling at -195 degrees Fahrenheit (-125 degrees Celsius).
Jupiter
Jupiter’s rapid rotation contributes to its short day length, and its core-generated heat keeps the planet warmer than expected for a gas giant.
Saturn
Saturn, despite its distance from the Sun, has a day length similar to Jupiter’s. Its frigid temperatures around -288 degrees Fahrenheit (-178 degrees Celsius) can be attributed to its distance from the Sun.
Uranus
Uranus’ axial tilt results in extreme seasons, leading to long periods of daylight and darkness. Its average temperature of -371 degrees Fahrenheit (-224 degrees Celsius) is due to its icy composition.
Neptune
Neptune’s temperature of around -353 degrees Fahrenheit (-214 degrees Celsius) results from its distance from the Sun and its methane-rich atmosphere. | Solar System Facts
As we venture farther from the Sun, Pluto’s highly elliptical orbit contributes to its extreme temperature swings, ranging from -375 degrees Fahrenheit (-225 degrees Celsius) to -400 degrees Fahrenheit (-240 degrees Celsius) | Solar System Facts
Space Exploration and Beyond: Unveiling the Mysteries
Humanity’s fascination with the solar system has led to numerous space missions that have expanded our understanding of the cosmos.
The exploration of the planets, their moons, and even their atmospheres has provided invaluable insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system.
Spacecraft like NASA’s Voyager probes have ventured far beyond the gas giants, sending back unprecedented images and data from the outer reaches of the solar system.
These missions have revealed the intricate details of Jupiter’s turbulent atmosphere, Saturn’s mesmerizing rings, and the unique features of Uranus and Neptune.
Robotic rovers, such as NASA’s Mars rovers Spirit, Opportunity, and Curiosity, have touched down on the Red Planet, exploring its surface and analyzing its geology.
These missions have provided evidence of past liquid water on Mars and paved the way for the search for signs of ancient microbial life.
More recently, NASA’s Juno spacecraft has been studying Jupiter up close, unraveling the mysteries of its magnetic field, atmosphere, and inner structure. Additionally, the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Rosetta mission successfully landed a probe on a comet, offering insights into the composition of these ancient remnants from the early solar system.
The future of solar system exploration is promising. Missions like NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) are set to peer deeper into space, unveiling more about distant planets, stars, and galaxies.
Planned missions to icy moons like Europa (a moon of Jupiter) and Enceladus (a moon of Saturn) hold the potential to uncover hidden oceans and potential habitats for life beyond Earth.
The Never-Ending Quest for Knowledge | Solar System Facts
In conclusion, the solar system remains a frontier of discovery, inviting us to unravel its secrets and understand our place in the universe. From the fiery surface of the Sun to the icy realms of Pluto, each celestial body offers a unique story about its formation, history, and evolution.
With each new mission and observation, we come closer to comprehending the complex interplay of forces that shaped our solar system.
As technology advances and our understanding grows, we are reminded that our exploration is boundless. The solar system is just one corner of the cosmos, and the mysteries that lie beyond are infinite.
Our journey of exploration and discovery will continue to expand our knowledge, challenge our perceptions, and ignite our curiosity for generations to come.
Searching for Life Beyond Earth: Possibilities on Other Planets | Solar System Facts
One of the most intriguing questions in the field of astronomy is whether life exists beyond Earth. While our current understanding is based on Earth as the sole harbor of life, the search for extraterrestrial life has expanded to include the investigation of other planets within our solar system.
Mars: A Potential Host for Life? | Solar System Facts
Mars has long been a focal point in the search for extraterrestrial life. Despite its harsh conditions, scientists have discovered evidence that suggests Mars may have once had liquid water on its surface. The presence of water raises the possibility that Mars could have supported microbial life in the past or potentially still does beneath its surface.
Recent discoveries of methane fluctuations in Mars’ atmosphere have also intrigued scientists. On Earth, methane can be produced by both geological processes and living organisms.
While the exact source of Mars’ methane is still debated, its detection opens the door to the tantalizing question of whether microbial life might be responsible
Icy Moons: Hidden Oceans of Potential | Solar System Facts
Two of the most promising locations for potential extraterrestrial life lie far from the Sun’s warmth: Europa, a moon of Jupiter, and Enceladus, a moon of Saturn. Both moons are believed to have subsurface oceans beneath their icy exteriors.
Europa’s ocean is kept in a liquid state by the gravitational interactions between the moon, Jupiter, and its neighboring moons. This ocean might offer a stable environment where life could thrive, shielded from the harsh radiation of space.
NASA’s upcoming Europa Clipper mission aims to study this moon in detail, searching for signs of habitability. Enceladus, on the other hand, has geysers erupting from its south pole, spewing water vapor and ice particles into space.
These geysers are believed to originate from an underground ocean. The Cassini spacecraft detected complex organic molecules in Enceladus’ plumes, raising the possibility that this distant moon could harbor the necessary ingredients for life.
Beyond Our Solar System: Exoplanets | Solar System Facts
While the focus has largely been on our solar system, astronomers have been making groundbreaking discoveries of exoplanets—planets orbiting stars beyond our Sun.
Some exoplanets lie within their star’s habitable zone, where conditions might be right for liquid water to exist on the surface—a key ingredient for life as we know it.
The study of exoplanets has opened up new avenues for investigating the potential for life beyond Earth. Instruments like the Kepler Space Telescope and its successor, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), have identified thousands of exoplanet candidates, some of which might possess the right conditions to support life.
The Quest Continues | Solar System Facts
While our understanding of the potential for life beyond Earth is still in its infancy, the search continues to capture the imagination of scientists and the public alike.
As technology advances and our exploration of the solar system and beyond expands, we may one day find ourselves with the answer to the age-old question: Are we alone in the universe? As we peer deeper into space and gain new insights into the conditions that could support life, we approach a new era of discovery—one that holds the potential to forever change our understanding of our place in the cosmos.
Diving Deeper: A Closer Look at Planetary Possibilities
In our quest to understand the potential for life on other planets, we delve into the characteristics of each celestial body in our solar system.
Mercury: A Challenging Environment | Solar System Facts
Mercury’s extreme temperatures and lack of a substantial atmosphere make it an inhospitable environment for life as we know it.
Its surface faces intense solar radiation and experiences extreme temperature shifts. With such harsh conditions, the likelihood of life on Mercury is considered extremely low
Venus: An Unforgiving Atmosphere | Solar System Facts
Venus’ thick, toxic atmosphere traps heat and creates a runaway greenhouse effect. Temperatures are hot enough to melt lead, and surface pressures are crushing. These extreme conditions make the survival of any known form of life impossible.
Mars: The Focus of Exploration | Solar System Facts
Mars, despite its current desolation, offers the most promise for potential habitability among the planets in our solar system.
The discovery of liquid water beneath its surface and evidence of past surface water support the idea that Mars might have been habitable in the past. Future missions seek to determine whether microbial life could exist below the Martian surface.
Solar System Facts
FAQ
1. Solar System Facts FAQ: What is a planet’s role in our universe?
Answer: Planets play a pivotal role as cosmic explorers, unveiling the marvels of space.
2. Solar System Facts FAQ: Are all planets scorching hot like Mercury?
Answer: Not all! While Mercury is blazing, others like Earth offer a perfect blend of warmth for life.
3. FAQ: Can we live on other planets?
Answer: Possibly! Mars shows promise, but challenges await our interplanetary dreams.
4. FAQ: Which planet showcases the most stunning rings?
Answer: Saturn steals the show with its breathtaking, ringed elegance.
5. FAQ: Do planets have personalities beyond their orbits?
Answer: Yes, each planet narrates a tale of extremes – from fiery Venus to icy Neptune.
6. FAQ: How does Jupiter protect us from space dangers?
Answer: Jupiter stands tall as our cosmic guardian, deflecting potential threats away from Earth.
7. FAQ: What’s the deal with Pluto’s demotion?
Answer: Pluto’s reclassification sparked debates, but its charm as a dwarf planet persists.
8. FAQ: Can planets beyond our solar system sustain life?
Answer: Exoplanets tease us with potential, leaving us to wonder about extraterrestrial neighbors.
9. FAQ: How does Earth stand out in the planetary crowd?
Answer: Earth boasts the ultimate blend: oceans, atmospheres, and diverse life forms.
10. FAQ: What future awaits our understanding of planets?
Answer: The cosmos holds limitless secrets, inviting us to keep gazing upward, and journeying onward.
